固体腫瘍プロジェクトのためのゲノムソリューション
genomicsHBRIの専門チームは、ゲノミクス分野での豊富な経験と、高度な機器群および堅牢な広範なパネル評価へのアクセスにより、固形腫瘍の臨床試験を最適化できます。また、固体腫瘍に関する国際的なガイドラインを継続的に検証し、既存のパネルをそれに応じて調整しています。
経験豊富な科学チームは、固形腫瘍の臨床試験に対して柔軟で迅速な対応を提供します。NGSがん治療の試験の約50%は現在、固形腫瘍によるものであり、広範なパネル型NGS評価を必要とする場合があることに注意してください。
体細胞変異の総数を評価する必要がありますか?あるいは、DNA配列の1つまたは複数のヌクレオチドの変化を決定できるだろうか?HBRIおよびCerba Healthcareのゲノミクス分野における経験と歴史のおかげで、広範なパネルNGS評価を提案できるようになりました。breastこれらは、肺、卵巣、乳房、大腸、悪性黒色腫、膀胱、消化管、およびまれな腫瘍(肉腫)における確立された、出現した、探索的な価値を持つ遺伝子の変化の大部分をカバーする可能性がある。
また、これらのパネルは、HRDスコア、TMBステータス、およびMSIも決定する場合があります。パネルは、以下のようながんの特徴を多く検出できるが、これに限定されない:
- 単一ヌクレオチド変異(SNV)
- 挿入物-削除(インデル)
- コピー番号のバリエーション(CNV)
- 遺伝子融合(転座)
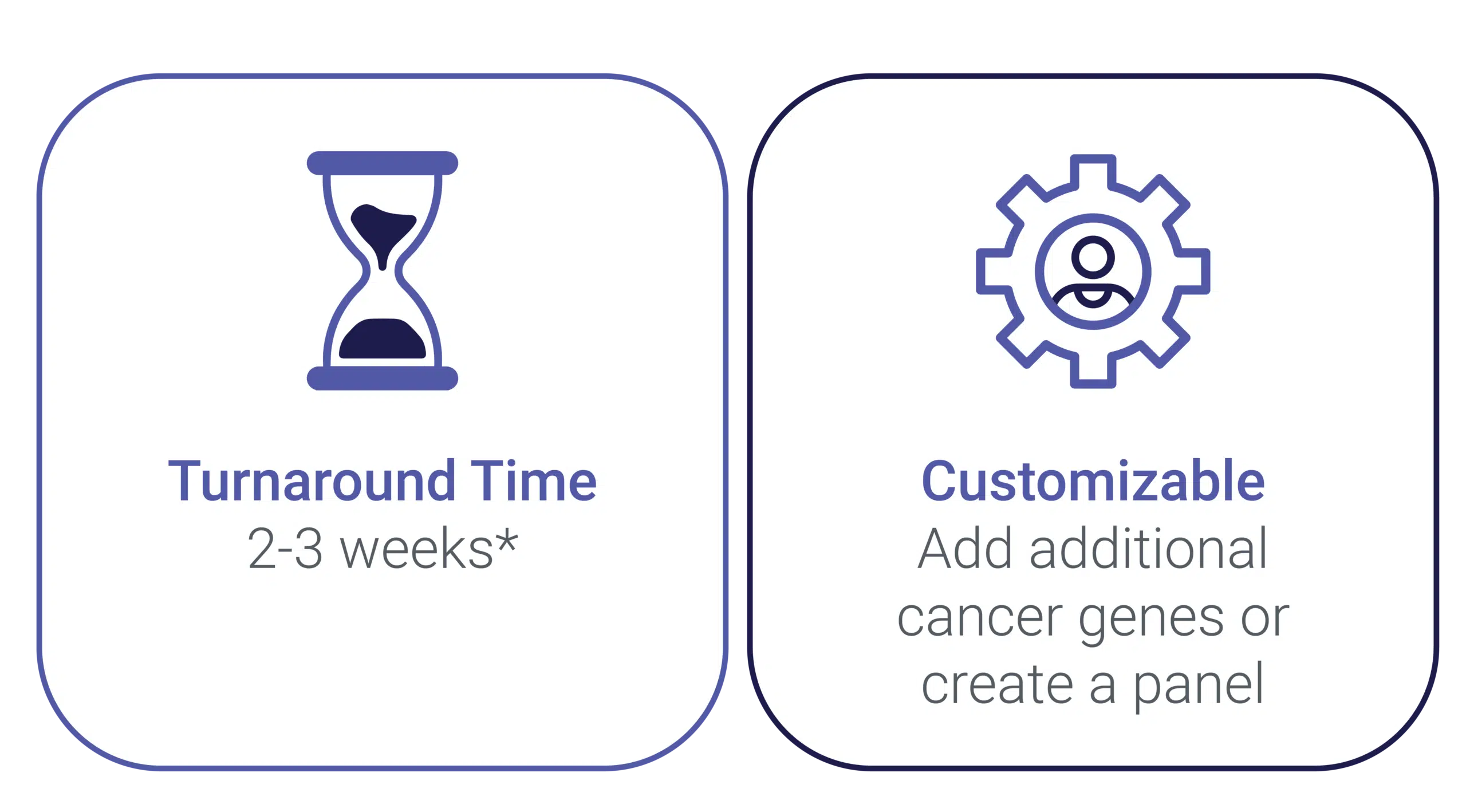
トライアルに応じて新しいパネルをカスタマイズできます
分析検証に十分な時間を科学プロジェクトに割り当ててください。NGSのアッセイがすでに試験の必要条件に従っている場合、承認されたサンプルの受領から結果までの所要時間は通常10〜15日です
セルバ・オンコサイン・パネル
42 DNA
17個のRNA(融合)
15種類のマイクロサテライト
がんの特徴
Cerba OncoSignのパネルは、肺、卵巣、乳がん、大腸、メラノーマ、膀胱、消化管などにおいて確立された変異や新たな価値を持つ変異を扱っています。MSI-Hも決定し、FFPE(OncoSign)および液体生検(OncoSign ctDNA)で実施されることがあります。また、ヨーロッパにおける定期的な臨床使用を目的として、FFPEでも実施されています。
EGFR(FFPE/リキッド生検)
エンドプレクシド
BRAF V600E
Amplifications: MET / HER2
Fusions: ALK / ROS1 / RET / NTRK1-2-3
Microsatellite instability (MSI) status may be provided by using the OncoSign panel.
Molecular Analysis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
With precision medicine becoming a more integral component of NSCLC treatment, molecular testing is an important step to help researchers, pathologists, and oncologists understand the genetic underpinnings of this devastating disease.
Discover how HBRI envisions the usage of an NGS-based broad panel assay to detect clinically relevant genetic alterations in NSCLC. Read our article on Precision medicine for NSCLC to find out more.

Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a modification that occurs in cancer cells where the number of repeated DNA bases in a microsatellite (a short sequence of DNA) is different from what it was when the microsatellite was inherited. MSI may be caused by DNA mistakes that are not corrected and is found most often in colorectal cancer, and endometrial cancer. Knowing whether a cancer has high MSI may be a predictive marker for response to checkpoint inhibitor regimens or clinical trial options.
Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) is an approximate measure of the total number of somatic mutations. Theoretically, high TMB levels will correlate with high neoantigen levels that will activate an antitumor immune response. TMB is currently an emerging immune biomarker for patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer based on clinical data. For example, tumors that have a high TMB appear to be more likely to respond to certain types of immunotherapy
A fusion gene is the juxtaposition of two otherwise separate genes, the transcription of which is translated into an abnormal protein (often a fusion protein that leads to a constitutive protein tyrosine kinase) that drives the growth of many cancers. The detection of fusion genes, also known as gene rearrangements, are important in targeted therapy clinical development and a great example of precision medicine. Such fusion genes may be ALK, ROS1 and NTRK1-3 to name a few.
Copy number variants (CNVs) refer to a circumstance to which the number of copies of a specific segment of DNA varies among different individuals’ genomes. Genetic variants, including insertions, deletions, and duplications of sections of DNA, are collectively referred to as CNVs. CNVs account for a large proportion of genetic variation between individuals and present a unique opportunity to investigate the impact of CNVs in drug development.
Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) is a DNA sequence variation that occurs when a single nucleotide, such as adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine, is altered. SNVs are sometimes referred to as single nucleotide polymorphisms.
The study of SNVs in clinical trials is relevant in providing information on disease risk assessment.
Cerba Paris: Our Comprehensive Oncopanels
| Genes | Cancer Type | Instrument | TAT* | Bone marrow | ctDNA | FFPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerba OncoSign | 59 | Solid tumors (important hallmarks of cancer) 42 DNA 17 RNA (fusions) 15 microsatellites HRD status (CE-IVD marked & in a separate panel) | NextSeq | 15 | X | X | |
| Cerba OncoSign 600+ | 658 | Solid tumors (important hallmarks of cancer) 638 DNA 20 RNA (fusions) TMB, MSI, HRD | NextSeq | 15 |
Taiwan Lab: Our Comprehensive Oncopanels in collaboration with ACT Genomics
| Genes | Cancer Type | Instrument | TAT* | Bone marrow | ctDNA | FFPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTOnco®+ (DNA-based) | 440 | Solid tumors (important hallmarks of cancer) TMB | Ion Torrent | 15 | X | X | |
| ACTDrug® (DNA-based) | 40 | Solid tumors (screening of actionable genes) | Ion Torrent | 15 | X | ||
| ACTFusion™ (RNA-based) | 31 | Solid tumors (actionable fusion genes) | Ion Torrent | 10 | X | ||
| ACTBRCA® (DNA-based) | 2 | Solid tumors (gene alterations to evaluate PARP inh) | Ion Torrent | 10 | X | X | |
| ACTHRD™ (DNA-based) | 24 | Solid tumors (gene alterations to evaluate PARP inh) | NextSeq 550 | 10 | X | ||
| CTRisk™ (DNA-based) | 32 | Identifies genetic alterations related to hereditary cancers | NextSeq 550 | 10 | X |
Reach out to our genomics team and see how we can help advance your research in the field of Solid Tumor NGS

